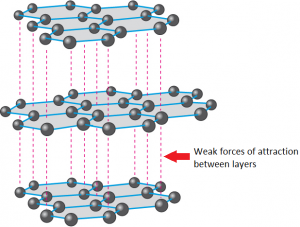
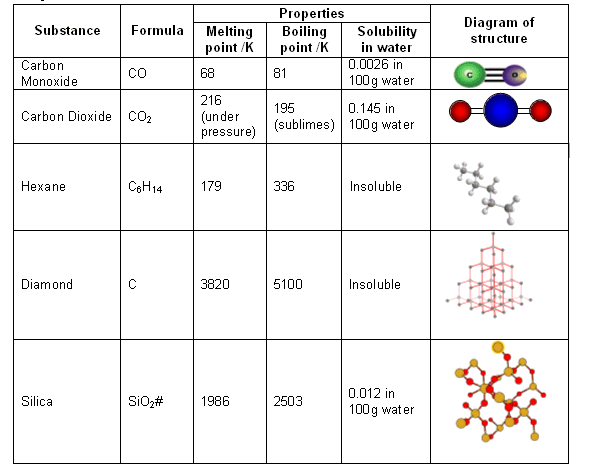
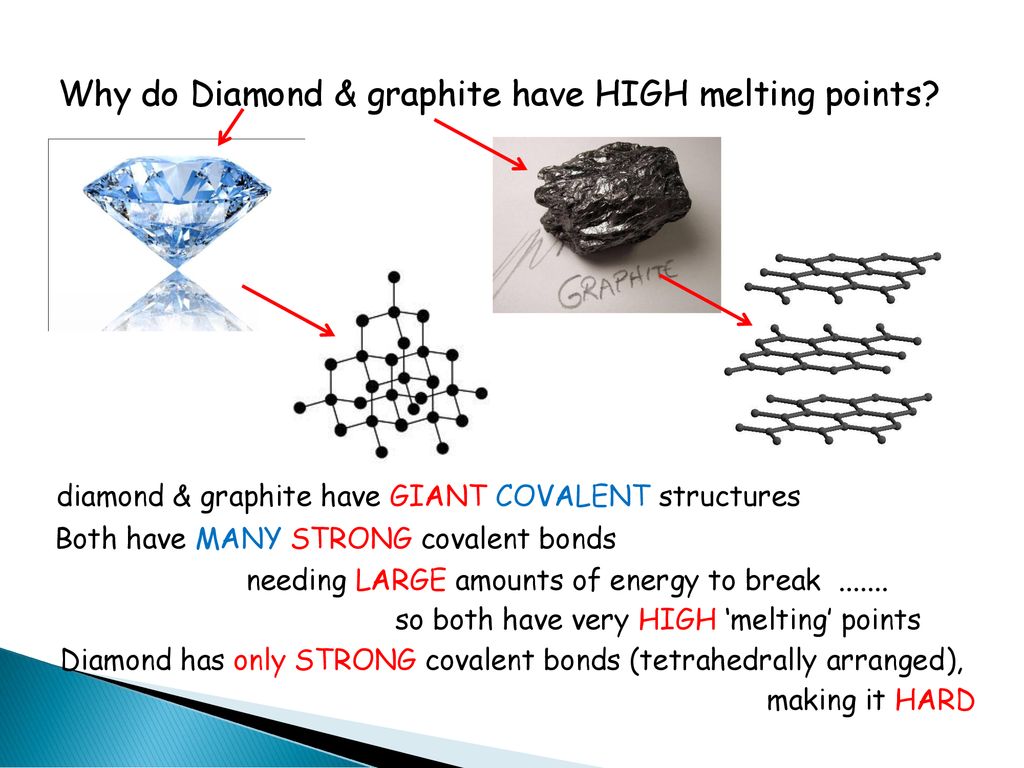
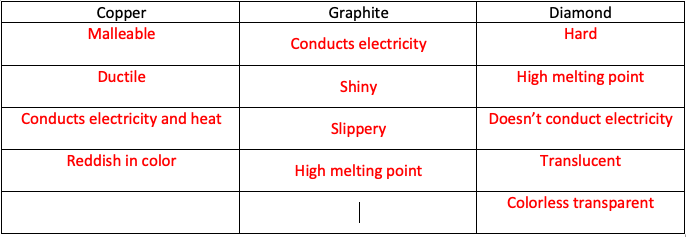
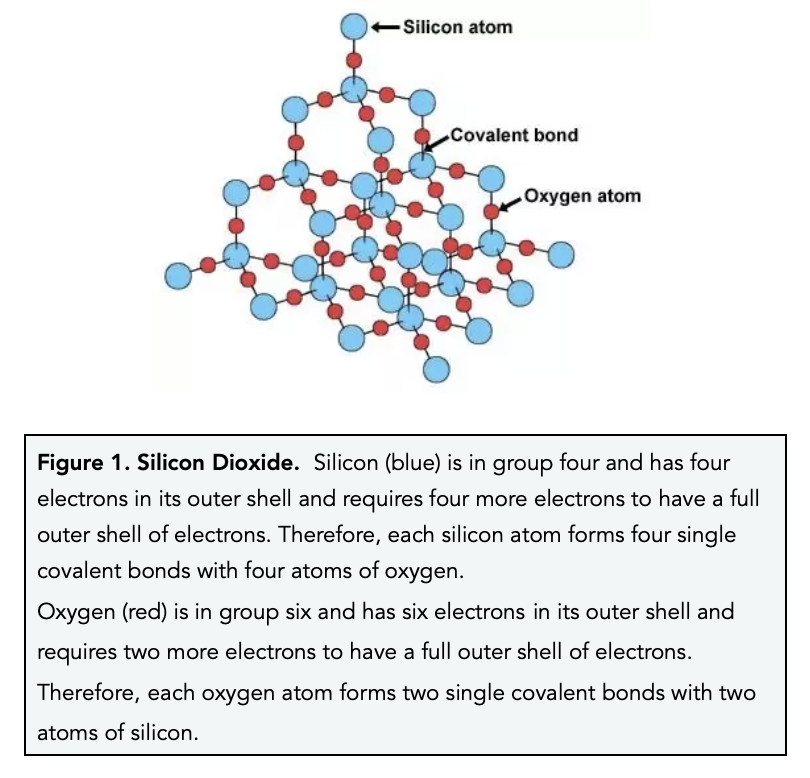
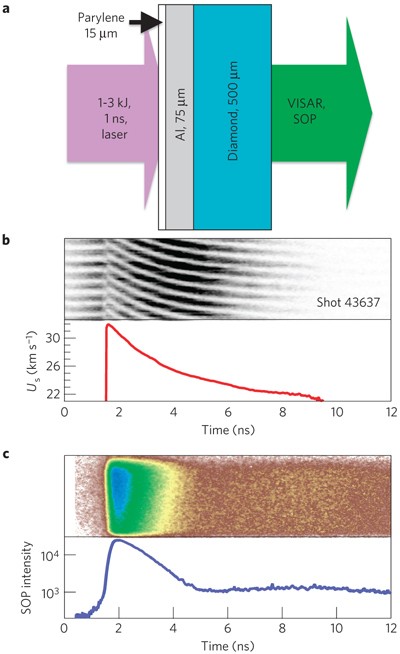
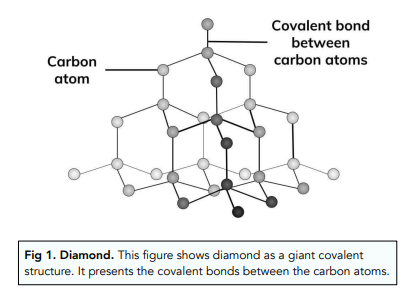
Carbon under extreme conditions: Phase boundaries and electronic properties from first-principles theory | PNAS

THE BEST SCIENTIST IS OPEN TO EXPERIENCE AND BEGINS WITH ROMANCE - THE IDEA THAT ANYTHING IS POSSIBLE. - Ray Bradbury – DON'T SAY YOU DON'T HAVE ENOUGH. - ppt download

At roughly what temperature and pressure will diamond graphite and liquid carbon all exist at equilibrium? | Homework.Study.com

Energies of diamond, graphite and polymeric chain as a function of the... | Download Scientific Diagram